







 X
X







 GLOBAL / ENGLISH
GLOBAL / ENGLISH

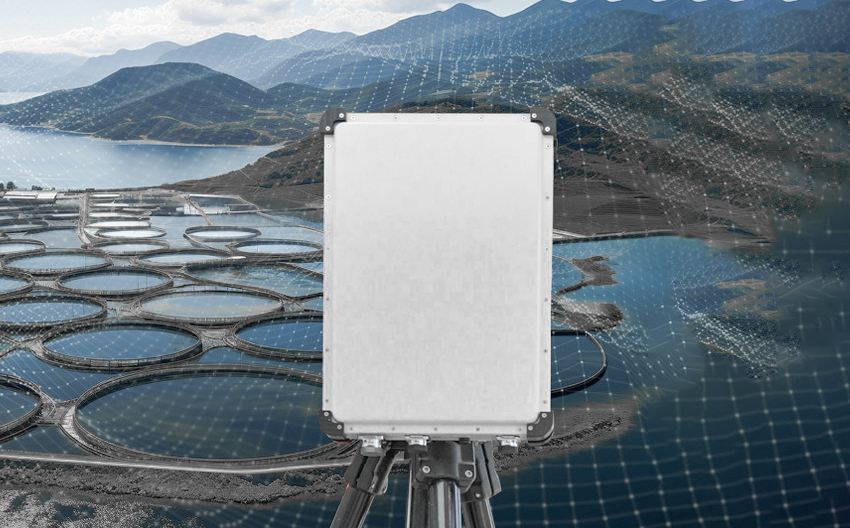
With the rapid advancement of drone technology, drones are evolving towards miniaturization, low-altitude operation, simplification, low-tech solutions, and cost-reduction. They offer several advantages such as high altitude operation, long-range vision, fast movement, obstacle-free travel, strong adaptability, and easy modification. Consequently, the use of drones is becoming increasingly widespread. However, the extensive use of drones has also sparked a series of security and privacy issues. To maintain public safety and protect sensitive locations, even personnel and critical targets in battlefields and strategic military sites, drone countermeasure systems are being widely deployed. These systems primarily include detection and interference. Successful interference must be based on the successful detection of drone targets.
Let’s explore the differences between passive and active drone detection. Sometimes, people ask, "What is the difference between passive and active drone detection?" In some cases, there is a misunderstanding about the meaning of these terms.
"Active drone detection" is sometimes mistakenly thought to refer to systems that can "read" the radio signals between a drone and its control station. This process is often called "decoding." Decoding RF signals is a complex process that involves receiving signals, demodulating to retrieve the baseband signal, and further processing to extract the information originally transmitted. The exact steps and methods depend on the modulation type and the nature of the transmitted data.
Similarly, "passive drone detection" is sometimes mistakenly thought to refer to systems that do not read the radio signal content between a drone and its control station.
Below are general definitions and examples of these two terms for further reference.
Active Drone Detection
Active drone detection involves emitting signals to detect the presence of drones. The system emits radio waves or light pulses, which reflect off objects and return to the sensor, providing information about the object's location and movement.
According to NASA, "Active sensors emit energy pulses and detect changes in the returning signal."
Examples of active drone detection methods:
Radar emits radio waves that reflect off objects and return to the sensor, providing information about the object's location and movement.
LiDAR emits light pulses that reflect off objects and return to the sensor, providing information about the object's location and movement.
Active drone detection methods carry risks in military operations because the emitted signals can be detected by adversaries.
Passive Drone Detection
Passive drone detection involves methods that do not emit any signals to detect drones and/or their controllers.
NASA states on its website, "Passive sensors can detect the energy emitted or reflected by an object."
Examples of passive drone detection methods:
RF drone detection systems receive and analyze communication signals between a drone and its controller.
Acoustic sensors receive and analyze sounds emitted by drone motors and propellers.
Cameras detect drones by capturing and, in some cases, analyzing images or videos of the surrounding area. These can be standard optical cameras and/or more advanced systems such as infrared cameras used for night vision.
Passive radar systems detect and analyze signals reflected from other electromagnetic sources. They provide information about an object's location and movement without needing to emit their own signals.