







 X
X







 GLOBAL / ENGLISH
GLOBAL / ENGLISH

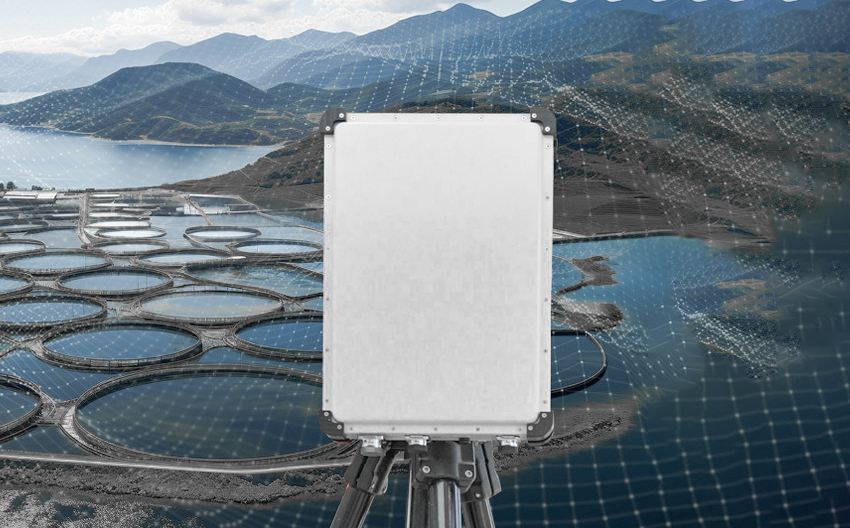
Drone detection devices operate based on several key technologies that can be used independently or combined to provide a more comprehensive drone detection capability. Here are some common drone detection technologies and how they work:
Radar Systems:
Working Principle: Radar systems operate by emitting electromagnetic waves and then receiving the signals that are reflected back. When these waves encounter an object, such as a drone, they are reflected back to the radar antenna and detected. Radar systems can measure the delay and changes in these reflected waves to determine the drone's position, speed, and direction of movement.
Radio Frequency (RF) Detection:
Working Principle: RF detectors detect specific radio frequencies used by drones for communication and navigation. Drones typically use radio signals to control flight and transmit video data; RF detectors can identify the source of these signals, thereby determining the presence and approximate location of the drone.
Acoustic Detection:
Working Principle: Acoustic detection devices detect drones by analyzing patterns in environmental sound waves. The rotors or propellers of drones generate distinct noise patterns, and acoustic sensors can identify these patterns, allowing for the detection of drones even beyond visual or radar detection range.
Optical and Infrared Cameras:
Working Principle: Optical cameras rely on visible light to capture images, while infrared cameras detect infrared radiation emitted or reflected by objects. Drones can be detected by infrared cameras through their heat emission under various lighting conditions or by optical means. These cameras are often used in conjunction with image recognition software that can automatically identify drones in videos or photographs.
These detection technologies can be flexibly configured based on specific application scenarios and threat levels to build an effective drone monitoring and defense system. Each technology has its unique advantages and limitations, which is why they are often combined in practical applications to compensate for the shortcomings of a single technology.